FlatList component in React Native is a performance-improved component for rendering large scrollable lists of data.
It is designed for handling big datasets with efficient memory usage and performance optimization by lazy loading content and recycling views.
Basic Usage
First, we need to import the FlatList component from the core react-native package:
import { TouchableOpacity, FlatList } from 'react-native';
Next, provide an array of data and a renderItem function to render each item.
It is also recommended to provide keyExtractor for extracting a unique key. By default it checks item.key property, then item.id, and then falls back to the index.
const data = [
{ id: '1', title: 'Item 1' },
{ id: '2', title: 'Item 2' },
{ id: '3', title: 'Item 3' },
];
const ItemComponent = ({ item }) => (
<View>
<Text>{item.title}</Text>
</View>
);
export default function Example() {
return (
<FlatList
data={data}
renderItem={({ item }) => <ItemComponent item={item} />}
keyExtractor={item => item.id}
/>
);
}
Pull-to-Refresh
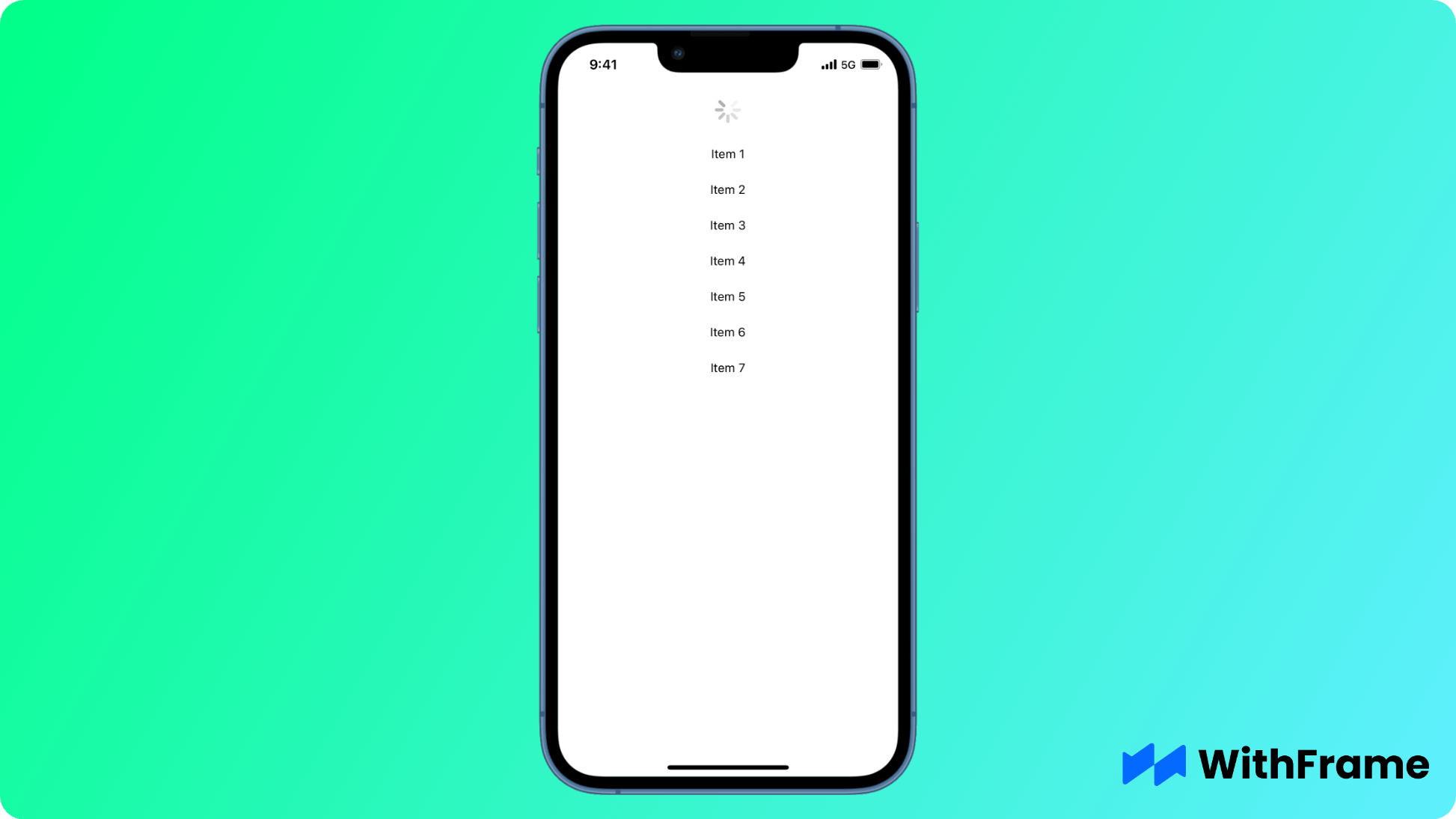
You can use refreshing and onRefresh props to implement the pull-to-refresh functionality in your React Native appication.
const [data, setData] = useState([
{ id: '1', title: 'Item 1' },
{ id: '2', title: 'Item 2' },
{ id: '3', title: 'Item 3' },
])
const [refreshing, setRefreshing] = useState(false);
const onRefresh = async () => {
setRefreshing(true);
// Async action to fetch new data
const response = await fetch('https://assets.withfra.me/api/posts.json')
setData(await response.json());
setRefreshing(false);
};
return (
<FlatList
data={data}
renderItem={({ item }) => <Text>{item.title}</Text>}
keyExtractor={item => item.id}
refreshing={refreshing}
onRefresh={onRefresh}
/>
)
Infinite Scrolling
To load more data as the user scrolls, use the onEndReached and onEndReachedThreshold props.
const [data, setData] = useState([
{ id: '1', title: 'Item 1' },
{ id: '2', title: 'Item 2' },
{ id: '3', title: 'Item 3' },
{ id: '4', title: 'Item 4' },
{ id: '5', title: 'Item 5' },
{ id: '6', title: 'Item 6' },
{ id: '7', title: 'Item 7' },
]);
return (
<FlatList
data={data}
renderItem={({ item }) => <Text>{item.title}</Text>}
keyExtractor={item => item.id}
onEndReached={async () => {
const response = await fetch('https://assets.withfra.me/api/posts.json')
setData([
...data,
...await response.json(),
])
}}
onEndReachedThreshold={0.5}
/>
)
Handling Empty Lists
FlatList accepts different components to render different parts of the list. For example, you can pass a ListEmptyComponent component to render when the data array is empty.
<FlatList
data={[]}
renderItem={({ item }) => <Text>{item.title}</Text>}
keyExtractor={item => item.id}
ListEmptyComponent={<Text>No data available.</Text>}
/>
Or, you can use ItemSeparatorComponent property to render a component between items.
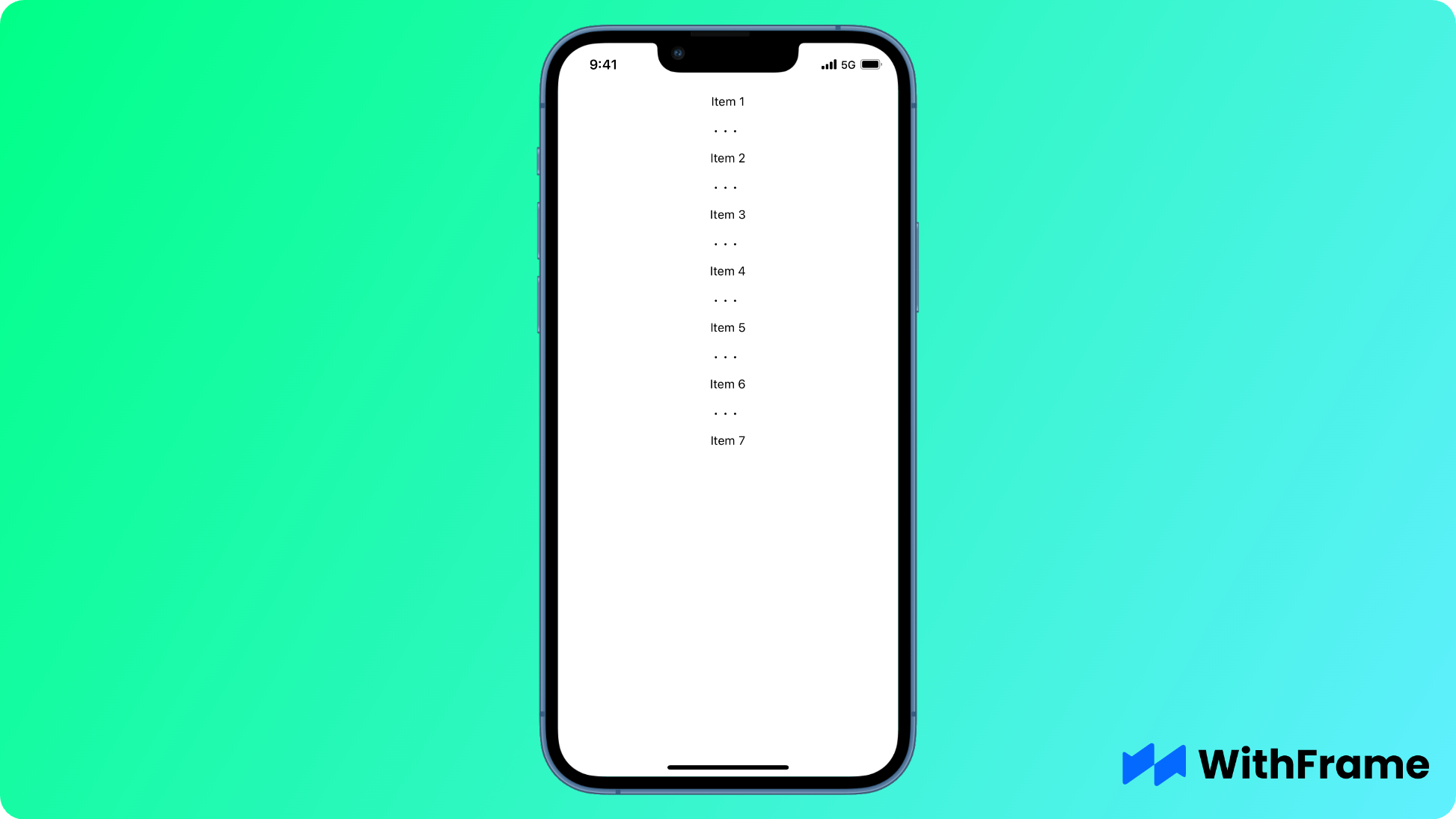
Notice that ItemSeparatorComponent is only rendered between the items, but not at the top or bottom.
<FlatList
data={data}
renderItem={({ item }) => <Text>{item.title}</Text>}
keyExtractor={item => item.id}
ItemSeparatorComponent={
<Text style={{ textAlign: 'center', letterSpacing: 6, fontSize: 20 }}>
···
</Text>
}
/>
Optimizing Performance
FlatList comes with several properties to optimize performance:
initialNumToRender- the number of items to render in the initial batch. By default it's10, but you can change this number to fit the screen but not much more.removeClippedSubviews- if you have a large list, setting this totruemight improve scroll performance.getItemLayout(data, index)- optional optimization function to skip content measurement step. This is only useful if all of the items have the same height (ITEM_HEIGHTin the example below).
<FlatList
data={data}
renderItem={({ item }) => <Text>{item.title}</Text>}
keyExtractor={item => item.id}
getItemLayout={(data, index) => (
{length: ITEM_HEIGHT, offset: ITEM_HEIGHT * index, index}
)}
/>